Most Mass-Produced US Naval Ships in WWII – World War II marked a pivotal era in naval warfare, demanding unprecedented production of diverse and technologically advanced ships by the United States. The effectiveness of the U.S. Navy rested significantly on its ability to mass-produce various vessel types, ranging from aircraft carriers to landing craft.
This introduction explores the critical role played by these ships, emphasizing their collective impact on the outcome of the war. From the sprawling decks of aircraft carriers facilitating strategic air power projection to the formidable firepower of battleships and the stealthy maneuvers of submarines, each vessel was a crucial cog in the wartime machinery.
This concise overview delves into the challenges and triumphs of mass production, underscoring the vital contribution of the United States’ naval fleet in securing victory during one of the most defining periods in modern history.
Importance of mass production for wartime efforts
Mass production played a pivotal role in the success of wartime efforts during World War II, offering several key advantages:
- Scale and Speed: Mass production allowed for the rapid and large-scale manufacturing of military equipment, including ships, aircraft, weapons, and vehicles. This speed was critical in responding to the urgent demands of a global conflict.
- Economic Efficiency: By streamlining production processes and standardizing components, economies of scale were achieved, making the manufacturing process more cost-effective. This efficiency ensured that resources could be allocated to various fronts without compromising the overall war effort.
- Increased Output: Mass production significantly increased the output of essential war materials. This was crucial in providing the vast quantities of ships, weaponry, and equipment needed to sustain military operations on multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Technological Advances: Mass production often drove technological innovation. As manufacturers sought to produce goods more quickly and efficiently, they frequently developed new and improved methods, contributing to the overall technological progress during the war.
- Logistical Advantage: The ability to produce large quantities of standardized equipment simplified logistics and supply chain management. Standardized parts and components allowed for easier maintenance, repair, and replacement of military hardware in the field.
- Strategic Flexibility: Mass production provided the flexibility to adapt to changing wartime demands. The ability to quickly adjust production lines based on evolving strategic needs allowed for a more dynamic response to shifting priorities on the battlefield.
Also, Read – Iconic Aircraft That Have Stood the Test of Time
Most Mass-Produced US Naval Ships in WWII
Fletcher-class Destroyers
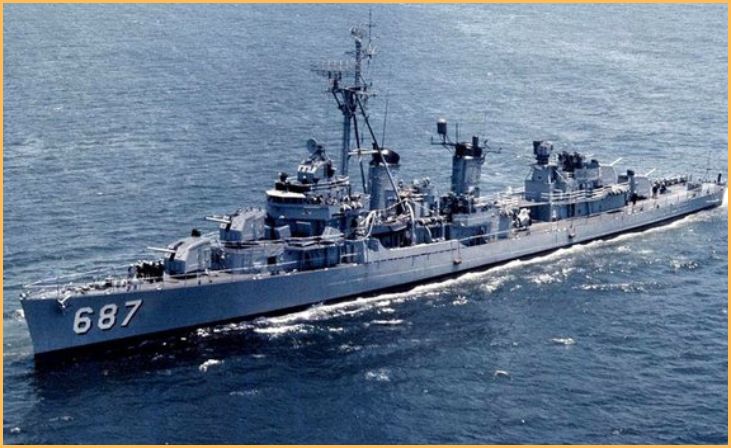

The Fletcher-class destroyers, a staple of the U.S. Navy in World War II, were versatile vessels crucial to naval operations. With over 170 units produced, they excelled in anti-submarine warfare, convoy escort, and shore bombardment.
Known for their speed, firepower, and reliability, these destroyers played a pivotal role in the Pacific and Atlantic theaters. Their adaptability and effectiveness in various roles made them a mainstay in the U.S. Navy’s fleet, contributing significantly to the Allied victory.
Essex-class Aircraft Carriers
The Essex-class aircraft carriers, integral to U.S. naval power in World War II, were a formidable fleet of carriers renowned for their role in the Pacific theater. With 24 carriers constructed, they formed the backbone of the U.S. Navy’s carrier force.
These carriers, including the USS Essex and USS Yorktown, played pivotal roles in major battles like Midway and Okinawa. Their ability to accommodate a large air wing, combined with advanced technology and durability, ensured air superiority and contributed significantly to Allied success.
The Essex-class carriers exemplified American naval strength and innovation during one of history’s most critical conflicts.
Liberty Ships
Liberty Ships were crucial to the Allied war effort in World War II, epitomizing mass production and efficiency. With over 2,700 built, they were essential cargo vessels designed for rapid assembly. Their simple design and standardized components allowed for quick construction, addressing the urgent need for maritime transport.
Named after prominent Americans, Liberty Ships played a vital role in supplying troops and materials to theaters of war, aiding in the logistical demands of global conflict.
Although not without challenges, such as the early welding issues known as the “Liberty ships’ brittle steel,” they significantly contributed to overcoming supply challenges and ensuring the success of Allied operations.
Landing Ship, Tank (LST)
The Landing Ship, Tank (LST), emerged as a critical amphibious warfare asset in World War II. Over 1,000 LSTs were constructed, embodying the innovation required for large-scale amphibious assaults.
Characterized by their ability to beach and unload directly onto shore, these vessels played a pivotal role in the D-Day landings and Pacific island-hopping campaigns.
With their substantial cargo capacity, LSTs transported tanks, vehicles, and troops, facilitating rapid and efficient amphibious operations. Their adaptability and contribution to successful beach landings made LSTs indispensable in projecting Allied power during key wartime engagements.
Gearing-class Destroyers
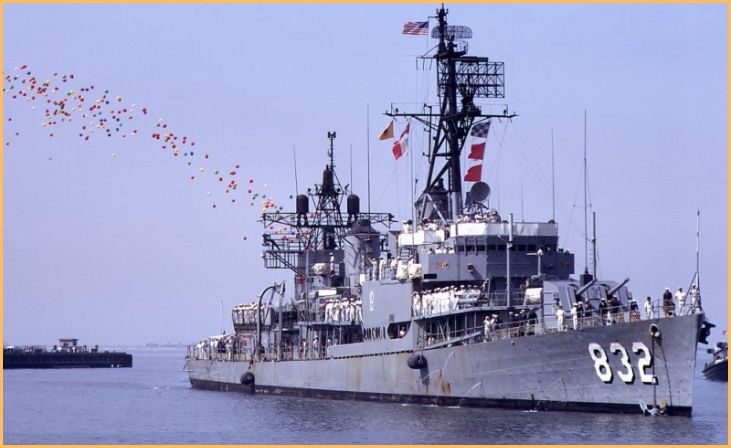

The Gearing-class destroyers, successors to the Fletcher-class, were instrumental in U.S. Navy operations during and after World War II. With over 90 ships commissioned, they represented an evolution in destroyer design.
Notable for their anti-submarine capabilities, increased firepower, and enhanced electronics, the Gearing-class destroyers were versatile assets in naval warfare. They played vital roles in the Korean and Vietnam Wars, serving as escorts, shore bombardment platforms, and anti-aircraft defenders.
The Gearing-class destroyers exemplified the post-World War II modernization efforts, contributing to the U.S. Navy’s continued effectiveness in evolving geopolitical landscapes.
Also, Read – Most Famous Paintings in the World
Iowa-class Battleships
The Iowa-class battleships, including the USS Iowa, USS New Jersey, USS Missouri, and USS Wisconsin, were formidable symbols of American naval power during World War II and beyond. Commissioned in the 1940s, these battleships were unparalleled in firepower and survivability.
Armed with nine 16-inch guns, they served in the Pacific theater, engaging in crucial battles like Okinawa and supporting amphibious landings. The USS Missouri gained historical significance as the site of the Japanese surrender in 1945.
Reactivated during the Korean War and Gulf War, the Iowa-class battleships remained potent symbols of American military might, representing a pinnacle in battleship design and capability.
Baltimore-class Cruisers
The Baltimore-class cruisers were a vital component of the U.S. Navy during World War II, comprising heavy cruisers armed with 8-inch guns. With 14 ships constructed, they excelled in roles such as shore bombardment, anti-aircraft defense, and surface warfare.
These cruisers, including the USS Baltimore and USS Boston, played essential roles in major Pacific and Atlantic campaigns. Versatile and well-armored, they provided critical support in amphibious landings and contributed to the overall success of naval operations.
The Baltimore-class cruisers showcased a balanced design, combining firepower, protection, and mobility, making them significant contributors to the U.S. Navy’s capabilities in mid-20th-century naval warfare.
Landing Craft, Infantry (LCI)
The Landing Craft, Infantry (LCI), served as pivotal assets in amphibious operations during World War II. Over a thousand LCIs were constructed, designed for the direct transport of infantry to enemy-held shores.
These vessels, equipped with the capability to beach and unload troops swiftly, played a crucial role in the Pacific and European theaters. Often modified for various roles, LCIs were employed in key operations like the Normandy landings and island assaults in the Pacific.
Despite their modest size, LCIs significantly contributed to the success of amphibious warfare, delivering infantry directly to the front lines and supporting the broader strategy of Allied forces during the war.
Sumner-class Destroyers
The Sumner-class destroyers, an improved iteration of the Fletcher-class, were essential components of the U.S. Navy’s post-World War II fleet. With a production run exceeding 60 ships, they represented advancements in anti-submarine warfare capabilities and electronics.
Commissioned in the late 1940s, Sumner-class destroyers played versatile roles, including anti-submarine and anti-aircraft duties. Their notable features included increased speed and enhanced radar systems.
These destroyers contributed to Cold War naval strategies and participated in conflicts like the Korean and Vietnam Wars. The Sumner-class destroyers were crucial assets, embodying technological advancements and adaptability in naval operations during the mid-20th century.
Gato-class Submarines
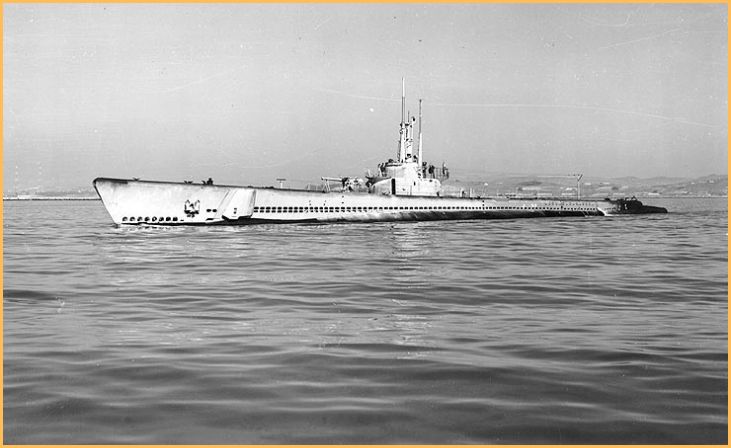
The Gato-class submarines were pivotal in U.S. naval strategy during World War II, representing a significant portion of the submarine fleet. With over 70 submarines constructed, they played a vital role in disrupting Japanese maritime supply lines in the Pacific.
These submarines, armed with torpedoes and equipped for extended patrols, were instrumental in reconnaissance and engaging enemy ships.
Notable for their reliability and endurance, the Gato-class submarines contributed to the success of submarine warfare in the Pacific theater. Post-war, they remained in service and influenced the design of subsequent submarine classes, showcasing their enduring impact on naval capabilities and tactics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the unparalleled scale and efficiency of mass production were decisive in shaping the outcome of World War II. The ability to swiftly manufacture and deploy ships, weaponry, and equipment provided a strategic edge, contributing to the Allies’ victory.
The wartime lessons of mass production continue to influence industrial practices and underscore its pivotal role in times of global conflict, emphasizing the enduring impact of streamlined, high-volume manufacturing on the course of history.
FAQs
Mass production played a crucial role by ensuring a rapid and large-scale manufacturing of ships and equipment, allowing the US to meet the demands of a global conflict, increase output, and provide economic efficiency.
Challenges included overcoming shortages of raw materials, coordinating complex supply chains, and adapting production lines to evolving wartime needs. Shipyards also faced the need for skilled labor and overcoming production bottlenecks.
Aircraft carriers were pivotal, providing strategic air power projection. The Essex-class carriers were a notable example, mass-produced to support naval operations in both the Pacific and Atlantic theaters.







